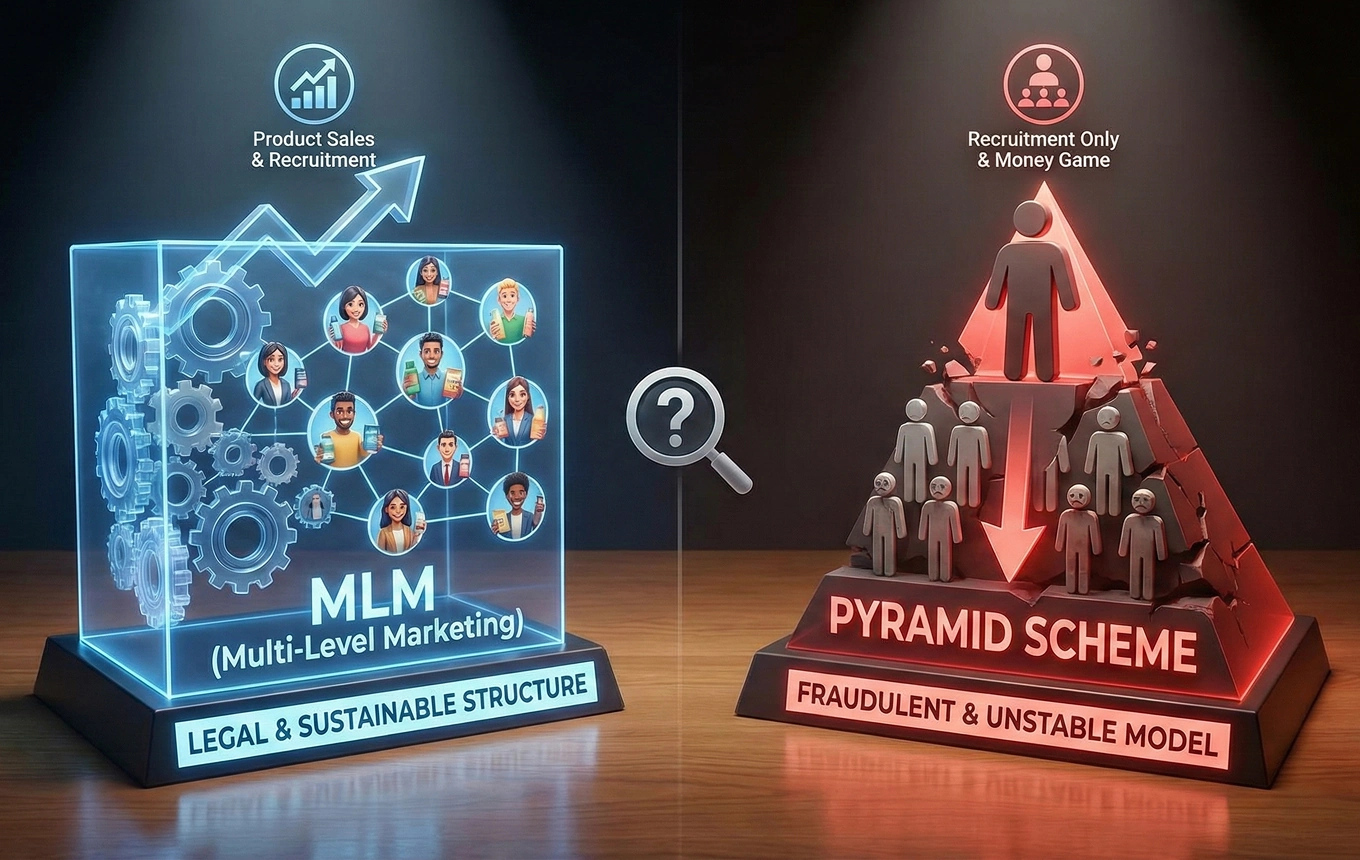
As network marketing continues to grow, many people still struggle to clearly tell the difference between a legitimate MLM business and an illegal pyramid scheme. This guide explains how both models really work, how money flows, whether MLM is legal, and how to spot warning signs before joining any opportunity.
You’ll also learn how modern MLM software supports compliance, transparency, and scalable growth, helping you build a trustworthy and future-ready network marketing business.
📋 In This Guide
- What Is MLM (Multi-Level Marketing)?
- How Legitimate MLM Companies Generate Revenue
- What Is a Pyramid Scheme?
- MLM vs Pyramid Scheme: Side-by-Side Comparison
- Key Differences Between MLM and Pyramid Schemes
- Is MLM Legal?
- What Makes an MLM Company Compliant?
- Warning Signs of a Pyramid Scheme
- Why the Confusion Between MLM and Pyramid Schemes Still Exists
- How to Evaluate an MLM Company Before Joining
Multi-level marketing (MLM), also called network marketing, is a business model where independent distributors sell products or services directly to customers and earn commissions from their own sales.
In some MLM compensation plans, they can also earn additional income from the product sales generated by the team they introduce.
Unlike traditional retail businesses that depend on stores, distributors, and large advertising budgets, MLM companies grow mainly through direct selling, referrals, and relationship-based marketing. Distributors act as both customer-facing sellers and brand representatives.
How Legitimate MLM Companies Generate Revenue
A compliant MLM company generates revenue primarily from:
- Sales of real products or services
- Ongoing purchases by customers who value those products
- Repeat orders from both retail customers and distributors who genuinely use what they sell
Importantly, revenue is not driven by recruitment fees or starter packages. If joining fees exist, they are usually limited to basic administrative costs such as starter kits or training material.
When a company cannot operate without constantly recruiting new distributors, it is no longer functioning as a true MLM.
The Role of Products in a Legitimate MLM
MLM products are central to every compliant network marketing business. In a healthy MLM structure:
- Products have real market value
- Pricing is reasonably competitive with similar products sold outside the MLM channel
- Customers would still buy the product even if there were no income opportunities attached
A strong indicator of legitimacy is when a company can clearly demonstrate retail sales to non-distributors. In other words, products are not used as a cover to justify recruitment — they are the real reason the business exists.
How Distributors Earn Money in MLM
In a legitimate MLM compensation plan, income is based on sales performance, not recruitment. Typically:
- Distributors earn commissions on products they personally sell
- Additional bonuses may be paid when their team sells products
- Team rewards are calculated using verified product sales volume
Most importantly, recruiting someone by itself does not generate income. Commissions only appear when real product sales take place. This principle is one of the most important distinctions in the MLM vs pyramid scheme debate.
Build a transparent and fraud-resistant MLM system with secure, traceable transactions and automated commission logic.
Read More
Why Blockchain-Powered MLM Software Could Redefine Trust in Network Marketing
What Is a Pyramid Scheme?
A pyramid scheme is an illegal business model in which participants earn money mainly by recruiting new members rather than by selling real products or services to customers.
Although pyramid schemes often look similar to MLM on the surface, the financial structure is fundamentally different. The business does not depend on consumer demand. Instead, it depends on a continuous flow of new participants paying to join.
How Money Flows in a Pyramid Scheme
In a typical pyramid structure:
- New participants pay joining, activation, or participation fees
- Those fees are distributed upward to earlier members
- Little or no revenue comes from genuine customers
The system does not create value. It simply redistributes money from later participants to earlier ones.
Recruitment-Driven Earnings
In a pyramid scheme, income is driven almost entirely by recruitment rather than real product sales. Your ability to earn is based on how many people you personally bring into the system and how many additional participants those recruits can enroll. As a result, financial success depends on expanding the network, not on building a customer base.
In practice, participants are commonly encouraged to:
- Recruit as many new members as possible to increase their earnings
- Buy multiple “positions” or “slots” inside the structure
- Pay extra fees to unlock higher commission levels
- Purchase large starter or upgrade packages in order to qualify for better payouts
Selling products to real customers is often treated as optional or unimportant, and most training and incentives focus on recruiting new participants instead of making real product sales.
The “Fake Product” Problem
Many modern pyramid schemes attach something that looks like a product in order to appear legitimate. These often include:
- Overpriced or low-quality physical products
- Digital memberships
- Generic training programs
- Access to private communities and webinars
In most cases, the product has little independent demand and is purchased mainly because it is required to remain eligible for commissions. The product exists to disguise a recruitment-driven money flow.
Why Pyramid Schemes Always Collapse
Pyramid schemes depend on unlimited recruitment, which is impossible in the real world. When the pool of new participants shrinks, incoming money slows down. Once this happens, the structure can no longer support payouts. As a result, the majority of participants — especially those who join later — lose money.
Turn your Shopify store into a fully automated direct selling platform with real-time orders, payouts, and distributor tracking.
Read More
Shopify MLM Integration Explained
MLM vs Pyramid Scheme: Side-by-Side Comparison
This comparison highlights the most practical difference between MLM and pyramid scheme models.
| Factor | MLM | Pyramid Scheme |
|---|---|---|
| Main revenue source | Product and service sales | Recruitment and joining fees |
| Role of products | Central to the business | Often symbolic or fake |
| Income model | Sales and team sales performance | Recruitment-driven |
| Sustainability | Can operate long-term | Collapses when recruitment slows |
| Legal status | Legal | Illegal |
Key Differences Between MLM and Pyramid Schemes
Product-Based Revenue
In a legitimate MLM, real customers exist outside the distributor network. Products compete in the open market based on price, usefulness, and quality. Even if recruitment slows down, the business can continue to operate because customers continue buying.
In a pyramid scheme, there is little or no genuine retail activity. Purchases usually happen only because participants are required to buy in order to remain eligible for commissions.
Legal Compliance and Regulation
A legitimate MLM company is structured to comply with consumer protection and direct-selling regulations. In the United States, misleading and deceptive business practices are overseen by the Federal Trade Commission.
Compliant MLM companies typically define:
- How commission calculations occur
- What qualifies as a valid sale
- How income claims may be promoted
- How refunds and returns are handled
Pyramid schemes usually avoid formal oversight. Company ownership and legal documentation are often unclear, and recruitment is commonly driven through private groups, messaging apps, and informal channels.
Compensation Structure
In legitimate MLM plans:
- Commissions are paid for products actually sold
- Team bonuses are based on verified product sales volume
- Rank advancement depends on measurable business activity
Recruiting someone does not produce income unless sales follow.
In pyramid schemes:
- Bonuses are triggered mainly by new sign-ups
- Participants are encouraged to purchase packages or positions
- Higher earnings require paying to unlock commission levels
Sustainability and Market Demand
Legitimate MLM businesses survive only when customers continue buying products they genuinely value. MLM software pricing must remain competitive, and products must solve real problems.
Pyramid schemes typically grow fast in the early stages and then slow abruptly when recruitment becomes difficult. Because the model depends on constant enrollment, collapse is unavoidable.
Consumer Protection
Reputable MLM companies offer:
- Clear refund and return policies
- Transparent income disclosures
- Written rules governing distributor conduct
In pyramid schemes:
- Refund terms are vague or missing
- Income claims are exaggerated
- No meaningful dispute resolution process
Empower your distributors to sell, recruit, and track performance from anywhere with a mobile-first MLM platform.
Is MLM Legal?
Yes. MLM is legal in many countries when companies follow consumer protection and direct-selling rules. For example, in the United States, this area is regulated by the Federal Trade Commission.
In general, regulators expect that:
- Income comes mainly from real product or service sales
- Recruitment incentives are secondary
- Marketing and income claims are truthful and verifiable
When these conditions are met, an MLM business can operate legally as a direct-selling model.
Check the legal framework, common risks, and practical compliance tips before launching or joining an MLM company in India.
What Makes an MLM Company Compliant?
A compliant MLM company is built around real product sales, customer protection, and transparent business practices. In general, a compliant MLM company shows:
Compliance Checklist
- Strong retail sales to real customers, not just purchases by distributors.
- Reasonably priced products that are competitive with similar market alternatives.
- Clear and written compensation plans explaining how commissions and bonuses are earned.
- Transparent income disclosures that reflect realistic earning outcomes.
- Fair refund and return policies for both customers and distributors.
Together, these factors indicate a product-driven and ethically operated MLM business.
Move from legacy systems to a scalable, enterprise-ready MLM platform without disrupting your operations.
Read More
MLM Software Migration Roadmap: When Your Startup Is Ready to Go Enterprise
Build a Compliant MLM Business
Get transparent commission tracking, fraud detection, and compliance tools designed for modern network marketing.
Warning Signs of a Pyramid Scheme
When reviewing any opportunity, look past the marketing and focus on how money is actually made. Pyramid schemes usually appear professional, but their structure depends on recruitment rather than real customer demand.
Be cautious if you notice:
Just to enter, hold a position, or qualify for commissions.
With most discussions centered on recruiting new members.
Such as fixed monthly earnings or quick financial freedom.
Instead of selling products and serving customers.
Where company ownership, legal registration, policies, or compensation details are hard to verify.
Future-proof your network marketing business with modern, flexible and decentralized-ready MLM infrastructure.
Read More
Is Decentralized MLM Software a Viable Trend or Just Hype?
Why the Confusion Between MLM and Pyramid Schemes Still Exists
The confusion continues largely because many past scams were promoted as network marketing opportunities. Some companies also deliberately copy the appearance of legitimate MLMs — using ranks, product catalogs, and commission charts — while violating the fundamental rules of product-based selling.
In addition, short-form social media content often oversimplifies the issue by claiming that all MLMs are scams or that pyramid schemes are misunderstood business models. Neither claim is accurate.
Discover how AI is changing commission automation, fraud detection, distributor insights, and performance analytics in modern MLM platforms.
Read More
AI in MLM Software Explained: Trends, Features & Top Platforms for 2025
How to Evaluate an MLM Company Before Joining
Follow these simple steps before joining any MLM opportunity:
Review the Compensation Plan
Confirm that commissions are earned mainly from real product sales and that bonuses are based on verified product movement, not on recruiting new members.
Check Real Product Demand
Look beyond the company’s own website and promotions. Independent reviews and customer feedback help confirm whether people buy the products for their value.
Verify Company Transparency
Make sure the company clearly publishes its corporate address, leadership team, distributor agreement, and official policies.
Review Refund and Return Policies
Read the return and buy-back rules carefully to understand your rights if you decide to leave or return products.
Confirm Legal Standing
Check public business records and consumer complaints, and do not rely only on testimonials from existing distributors.
Choose the Right MLM Software Pricing Model for Your Business
Compare pricing models and choose the right MLM software that fits your business stage, growth goals, and budget.
Conclusion
The key difference between MLM and pyramid schemes is how value is created. Legitimate MLMs focus on selling real products, offer transparent compensation and protect consumers, while pyramid schemes rely on recruiting and fees with little actual sales.
Compliant MLMs use clear business practices, fair payouts, and modern software for commission tracking, reporting, and compliance — ensuring ethical, product-driven growth.
In short, MLM can be legitimate if it emphasizes real customer demand, honest income potential, and transparency. Anything prioritizing recruitment over sales should be approached with caution.
Frequently Asked Questions